How to solve the problem of concave printing exhaust gas? The complete strategy from the source, process to the end treatment is here!
Gravure printing has the advantages of mature technology, high production efficiency, full and rich layers of printed products, and high reproducibility of original documents, and is widely used in the flexible packaging industry. Our company has 7 advanced gravure printing production lines at home and abroad, with an annual output of about 26000 tons of packaging film. In this article, the author combines gravure printing waste gas generation, production process control, equipment improvement, waste gas (VOCs) treatment, heat source utilization, and other aspects to conduct in-depth research on gravure printing waste gas (VOCs) emission reduction and energy-saving technologies, achieving significant economic and social benefits.
Source of gravure exhaust gas
The VOC content of solvent based ink used in gravure printing production process is ≤ 75%. To improve printing performance, various solvents (ethyl acetate, n-butanol, isopropanol, n-propyl acetate, etc.) need to be added to the ink for mixing and dilution. VOCs are evaporated and emitted during the ink mixing and drying process.
In order to reduce the generation of VOCs, the printing industry has developed rapidly in recent years in terms of controlling the source of exhaust gas using water-based ink (absorbent substrates ≤ 15%; non absorbent substrates ≤ 30%) technology. However, due to the incomplete technical difficulties in adhesion, water resistance, glossiness, and other aspects of water-based ink, its current application is still limited. This article is based on the solvent based ink widely used in gravure printing, and explores the research on VOCs emission reduction and energy-saving technologies.
Process control of gravure ink
01/Storage
VOCs such as ink and solvents should be stored in sealed containers, which should be covered and sealed to maintain airtightness, and stored in dedicated hazardous chemical warehouses. The temperature of the hazardous chemical warehouse should be controlled between 0 ° C and 28 ° C. The warehouse can also be equipped with a water storage roof or cooling water pipes on the roof. When the outdoor temperature is 30 ° C or above, water should be sprayed to cool down and keep the temperature inside the warehouse below 28 ° C. Conditional hazardous chemical warehouses should be equipped with explosion-proof air conditioning or explosion-proof air supply equipment to control the temperature below 28 ℃ in summer and above 0 ℃ in winter.
02/Allocation
The process of mixing ink and solvents should be carried out using automatic ink mixing equipment, operating in a closed space to reduce ink and solvent evaporation caused by exposure. If the conditions are not met, local gas collection measures should be taken in the isolation room, and the exhaust gas should be input into the VOCs exhaust gas treatment system through explosion-proof fans and sealed pipelines.
03/Ink supply
After ink mixing, it is recommended to use a closed pipeline to transport the ink to the printing machine unit (preferably using a self flowing type). The demand unit should use centralized viscosity control according to the usage amount, and use pneumatic valves to automatically add ink to the ink tray.
For transferring ink and solvents using non pipeline transportation methods, closed containers should be used. When adding ink or solvent to the ink tank, it is advisable to use a unit type ink viscosity controller to keep the solvent in a sealed state within the unit. After adding ink, the ink tank should be promptly covered to reduce the emission of VOCs during the ink supply process.
04/Printing
To reduce on-site volatilization of exhaust gas, cover plates should be added to ink trays, ink drums, and solvent drums. For gravure printing scrapers, closed scrapers should be preferred, or measures such as ink tank cover plates and changing the shape of ink tank openings should be taken to reduce the open area of the ink supply system. The printing process should adopt automatic control of ink viscosity to achieve online monitoring of ink viscosity and automatic solvent addition, reducing the frequency of manual opening of ink caps and minimizing VOCs volatilization.
The printing unit should adopt local gas collection measures, with suction ports set at the lower part and transmission side of the printing unit. After the exhaust gas is collected, it is discharged to the VOCs exhaust gas treatment system through a sealed pipeline.
05/Oven heating
The heating of the gravure printing oven accounts for about 70% of the overall fuel and power cost, and is a key focus of energy conservation and emission reduction. The new high-efficiency gas suspension or semi suspension oven has good drying and energy-saving effects; Conditional heating methods should prioritize air heat pumps or water electricity (steam) mixed modes. The inlet and return air ducts should use internal circulation function or LEL automatic control. The oven should be well sealed to reduce exhaust gas and heat loss caused by air leakage. During operation, the air volume should be adjusted to maintain a slight negative pressure inside the oven.
06/Version change cleaning
Gravure printing requires cleaning of the printing plate upon completion of the order or replacement of the product. When cleaning, try to use fewer solvents to quickly clean the plate roller during operation. If further cleaning is needed, it is advisable to use an ultrasonic cleaning machine in a closed space for automatic cleaning. The waste gas produced should be collected locally and discharged into the VOCs waste gas treatment system through a sealed pipeline.
Printing ink trays, ink tanks, cover plates, etc. can greatly reduce the volatilization of VOCs caused by the use of solvents during the cleaning process by spraying Teflon. By scientifically arranging production orders and using products of the same specifications and varieties for centralized production, the frequency of plate roller replacement is reduced, and the generation of VOCs waste gas is minimized.
07/Production Environment
The production environment for gravure printing should be controlled at a temperature of 18-28 ℃ and a humidity of 45% -65%. The indoor and outdoor environments should be kept in a slightly negative pressure state (indoor negative pressure) to reduce the overflow of VOCs.
Improvement of Printing Machine Exhaust System
The drying device consists of an oven, a fan, an air valve, an air duct, an air nozzle, etc. Hot air is directly blown onto the substrate through the nozzle, and the solvent film layer on the surface of the substrate is destroyed by the hot air jet. The solvent in the ink evaporates through the hollow medium holes to the outside of the ink layer, and a part of the heat is transferred in the form of latent heat. Another part of the heat is transferred inside the substrate through thermal conduction, and the remaining heat is ultimately carried out of the oven by air.
The hot air drying process of gravure printing equipment is a complex mass and heat transfer process. The quality of printing is not only related to the hot air speed, temperature, ink thickness, exhaust system, environmental temperature and humidity, but also greatly influenced by factors such as substrate characteristics, ink composition and characteristics, and drying oven structure.
In order to improve the comprehensive utilization rate of heat in the oven, we have taken the following improvement measures:
(1) Adopting an insulated oven, ceramic fiber felt insulation layer is used on the box wall, and it has a heat reflecting insulation effect to reduce heat loss in the drying system.
(2) The oven nozzle corresponds to the alloy guide roller of the printing machine, which absorbs and transfers heat through the metal guide roller, increases the contact area with the overprint material, and improves energy utilization efficiency.
(3) Install a return air heat exchanger to exchange heat between the exhaust air and the inlet air of the heating oven, recover the hot air from the exhaust, and achieve secondary circulation of hot air while reducing the solvent content in the inlet air. This method can recover about 65% of hot air and reduce waste air emissions by about 30%.
(4) Taking advantage of the low concentration of bottom exhaust and high concentration of upper exhaust, the bottom exhaust duct is introduced into the upper exhaust mode to reduce the indoor exhaust of the upper exhaust. After testing, each printing machine reduces the exhaust emissions by about 12000 cubic meters per hour.
(5) By utilizing unit or local LEL technology, the upper exhaust system can automatically adjust the circulating air volume based on concentration, reducing the amount of waste air emissions. This plan reduces 40% of exhaust emissions under stable operation conditions.
Design of VOCs treatment facilities
The VOCs exhaust gas from gravure printing has the characteristics of low concentration and high air volume. After comparing various schemes, we have chosen a two-stage zeolite rotary wheel concentration+three slot RTO (regenerative oxidation furnace) exhaust gas treatment system. Utilizing two-stage rotary wheel concentration to increase the concentration of VOCs in process gas, in order to achieve self-sustaining operation of RTO and reduce natural gas consumption.
The zeolite rotary wheel concentration removal efficiency is 90% to 95%. When the VOCs concentration in the exhaust gas exceeds 500mg/m ³, single-stage rotary wheel concentration adsorption can no longer meet the requirement of chimney exhaust VOCs concentration ≤ 40mg/m ³. Design a two-stage impeller to perform secondary adsorption on the gas adsorbed by the first stage impeller, increasing the adsorption efficiency of the impeller to 98.5% and significantly reducing VOCs emissions. Adopting a three slot RTO (regenerative oxidation furnace) design, the VOCs removal efficiency can reach over 99%, significantly improving the environment.
Energy saving of VOCs treatment system
Through the operation and management of the VOCs treatment system, equipment improvement, and energy recycling, VOCs emissions reduction and energy conservation can be achieved.
01/Double stage zeolite wheel concentration
The design of the two-stage zeolite wheel concentration device includes two first stage wheels (A1&B1) and two second stage wheels (A2&B2). The desorption air from the first stage wheel directly enters the RTO system, and the adsorption air from the first stage wheel enters the second stage wheel again to complete secondary adsorption (A1 adsorption air enters A2, B1 adsorption air enters B2). The adsorption air from the second stage wheel is directly discharged into the exhaust pipe, and the desorption air from the second stage wheel is introduced into the inlet of the first stage wheel to mix with the original process waste gas. (Figure 1 Schematic diagram of two-stage zeolite wheel concentration), the key points for energy-saving operation are as follows:
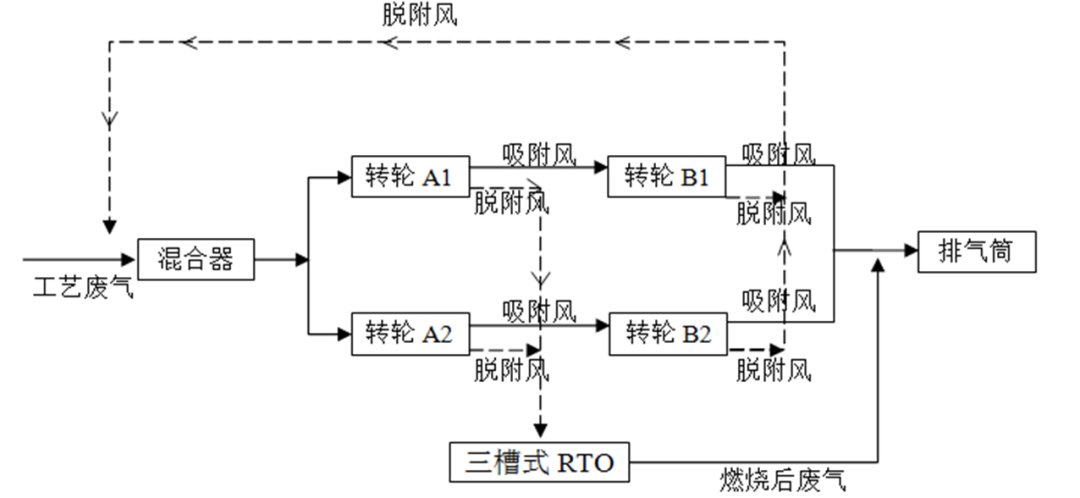
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of two-stage zeolite wheel concentration
(1) Wheel speed adjustment: When starting up, it is generally set at around 30HZ. During operation, it is adjusted according to the air volume. For example, when the air volume is low or the concentration is low, the frequency setting of the wheel rotation motor is adjusted to reduce the rotation speed and increase the concentration, achieving self balance of RTO combustion and saving natural gas; On the contrary, increase the rotational speed to enhance the wheel adsorption effect and ensure that the exhaust emissions meet the standards.
(2) Regular replacement of impeller inlet filter bag: The pressure difference at the impeller inlet should not exceed 75mmAQ. By regularly cleaning or replacing it, the pressure difference should be controlled below 25mmAQ as much as possible, which can save the power load of the system fan.
(3) Wheel temperature adjustment: The inlet temperature of the wheel detachment is set to 180 ℃, and the temperature is controlled at this location. It enters through the upper part of the RTO combustion chamber and uses a proportional valve and mixing box to stabilize the temperature control of the wheel detachment inlet. When the inlet temperature of the wheel desorption is below 115 ℃, it will cause low desorption efficiency; Exceeding 225 ℃ may pose a safety hazard. In this case, the equipment must be forcibly shut down and the high-pressure CO2 device must be automatically interlocked to cool down the rotor and ensure safety.
02/Three tank RTO (Regenerative Oxidation Furnace)
RTO (Regenerative Oxidation Furnace) includes three major functions: heat storage, thermal oxidation, and combustion. The "heat storage" comes from the heat storage body in RTO, and the domestic ceramic heat storage system has a heat utilization efficiency of over 97%. The working principle is to heat the organic waste gas to above 790 ℃, causing the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the waste gas to oxidize and decompose into carbon dioxide and water. The heat generated during the oxidation process is stored in the ceramic heat storage body, which heats up and stores heat. The heat stored in the ceramic thermal storage body is used to preheat the organic waste gas that enters later, which is the "heat release" process of the ceramic thermal storage body, thereby saving fuel consumption during the waste gas heating process.
The three slot RTO adopts valve switching. During the lucky period, it is divided into three stages and operates periodically. For example, in stage one, the exhaust gas is preheated through the heat storage tank 1 and then enters the combustion chamber for combustion. The exhaust gas is oxidized and decomposed in the combustion chamber (usually maintained at 800-850 degrees Celsius), and the residual untreated exhaust gas in the heat storage tank 2 is blown back to the combustion chamber for incineration treatment (blowing function). The decomposed exhaust gas is discharged through the heat storage tank 3, and at the same time, the heat storage tank 3 is heated (as shown in the schematic diagram of the three slot RTO in Figure 2).
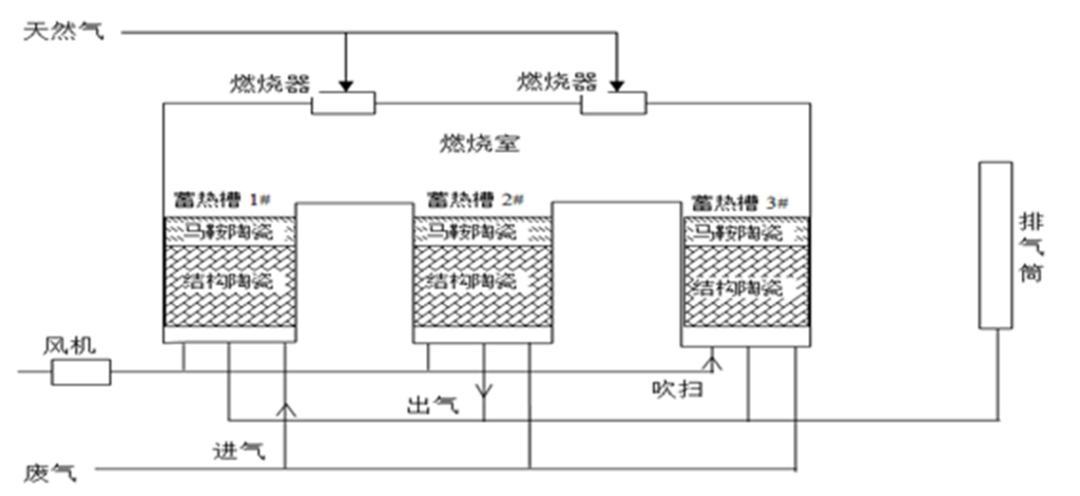
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of three slot RTO (regenerative oxidation furnace)
The operating energy consumption of RTO (Regenerative Oxidation Furnace) is mainly electricity and natural gas. Under the same working conditions, scientific operation management and improvement can achieve energy conservation and emission reduction:
(1) RTO switching valve time adjustment: When there is a large temperature difference or high temperature (such as exceeding 1000 ℃) between the RTO heat storage layer and the cooling zone, adjust and shorten the cycle of the RTO switching valve (usually set between 1.5 minutes and 2 minutes), so that the heat is evenly distributed throughout the combustion chamber, achieving RTO furnace temperature control and saving electricity costs.
(2) Adjust the inlet pressure: When there is a small temperature difference between the middle and upper layers of RTO or a high temperature in the middle layer (750 ℃), the pressure value of the system inlet can be adjusted to increase the frequency of the system fan, increase the temperature difference, reduce the middle layer temperature, and improve the efficiency of VOCs treatment; When there is a large temperature difference between the lower and middle layers of RTO, the pressure value at the air inlet can be adjusted to reduce the frequency of the system fan and save electricity consumption.
(3) Fresh air door renovation: RTO safety design, when the RTO combustion chamber temperature rises above the set value, the fresh air door will automatically open, reducing the combustion chamber temperature by entering low-temperature outdoor air, but increasing the exhaust gas treatment air volume. Through in-depth research, we have adopted a design that modifies the fresh air duct and uses bottom exhaust from the printing machine unit (at room temperature). This not only meets the cooling requirements but also reduces electricity consumption without increasing the amount of exhaust gas treatment.
(4) Shutdown operation: When the exhaust gas treatment system is shut down, the RTO temperature is maintained at 400 ℃. Due to the insulation effect of the internal heat storage layer, the natural gas consumption during restart is reduced.
03/Thermal cycle utilization
During the operation of the VOCs exhaust gas treatment system, the exhaust gas temperature in the chimney is around 200 ℃. To achieve full utilization of energy, heat exchange is installed on the pipes entering the chimney to recover the heat from waste discharge.
When designing a heat exchanger, dry burning and low-temperature protection measures must be considered. For example, the flue gas outlet temperature of a finned tube heat exchanger is continuously monitored by a thermal resistor. When the temperature is lower than the set temperature, the heat exchanger will be bypassed and the circulating water outlet temperature of the finned tube heat exchanger will be continuously monitored and controlled by the thermal resistor. When the temperature is higher than the set temperature, the heat exchanger will be bypassed. Figure 3 shows the principle diagram of VOCs heat recovery.
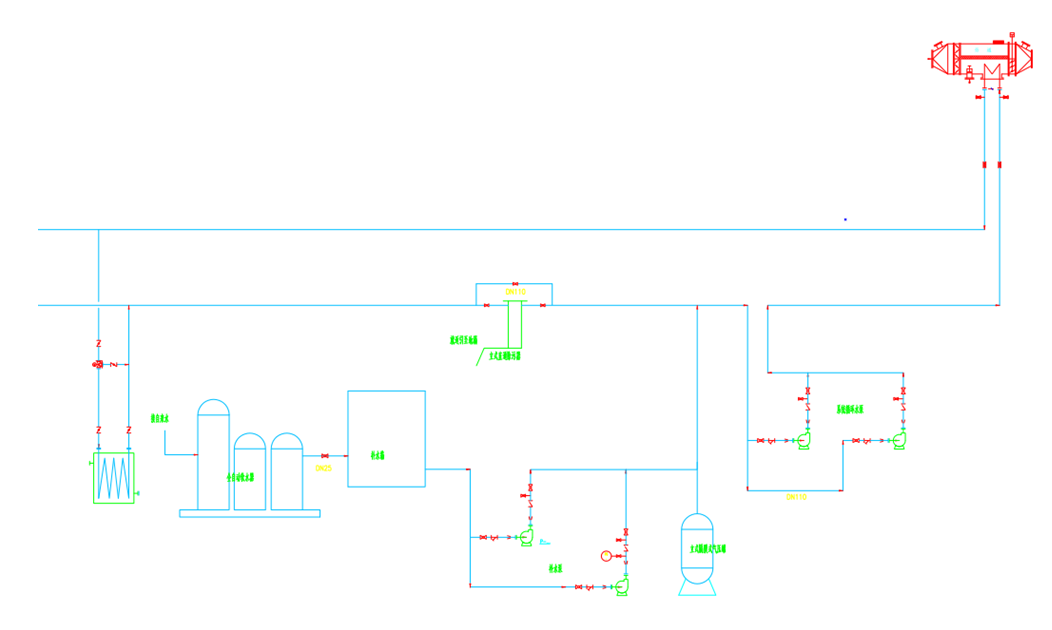
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of VOCs heat recovery
By controlling the pump and water storage tank through circulating water, the recovered hot water can be reused in the printing machine and added to the oven, reducing printing energy consumption. In winter, hot water is also used for heating production and office areas, achieving energy recycling.
maintenance
The VOCs waste gas treatment system has a complex structure, high degree of automation, and multiple safety interlocks. During operation, a comprehensive inspection should be conducted every two hours, and inspection records should be kept. Any abnormal noise, temperature rise, emission rate, etc. should be promptly arranged and dealt with. In addition to operational inspections, specialized inspection equipment such as infrared thermography, vibration testing instruments, ammeters, etc. should also be used for professional inspections to detect abnormal signs in advance, facilitate timely and effective measures, and ensure the continuous and stable operation of the VCOs exhaust gas treatment system. The daily maintenance points are as follows:
(1) Fans, gearbox motors: Important equipment can be measured online, while others are measured weekly; Lubricating oil should be added once every three months; The bearings should be replaced every 5 years.
(2) Automatic (pneumatic) valves: Compressed air pipelines are equipped with filters and drain valves; The air circuit uses specialized compressed air lubricating oil; Check the discharge of the instrument pressure regulating valve filter every week.
(3) Fan: The impeller of the fan is inspected and cleaned on site every six months due to the adhesion caused by smoke particles and other factors.
(4) ROT furnace body: The outer wall of RTO is coated with heat-resistant paint and inspected and repainted annually; Internally, open every two years to check the condition of the heat storage bricks, and repair or replace them according to the situation.
(5) Sealing: Check the sealing ring of the zeolite wheel, the transmission chain of the zeolite rotary motor, and the sealing components of the automatic regulating valve every six months.
(6) High temperature components: After about 2 years of operation, the RTO internal high-temperature probe will be replaced; Perform sealing and zero position calibration on high-temperature proportional valves, and maintain or replace the hot weather ignition switch system.
(7) LEL verification: VOCs waste air inlet LEL is verified once every quarter to avoid deviations that may affect system control accuracy.
(8) Circulating water: The heat recovery circulating water should be softened water or pure water, and should be completely drained and replaced during annual shutdown.
(9) Natural gas pressure gauges, safety valves, combustible gas alarms, compressed air pressure gauges, etc. must be calibrated and labeled strictly in accordance with legal and regulatory requirements.

