How can label printing companies use RFID to improve production convenience? See how this company does it.
In recent years, industries ranging from the vehicle access control systems we are familiar with, patient monitoring devices, to logistics and warehousing management have all been adopting RFID technology to facilitate people's lives and reduce staff workload. This has led to the rapid development of RFID technology, with its application areas becoming increasingly widespread.
Compared with traditional barcodes, RFID has obvious advantages in usage. In terms of physical characteristics, RFID chips are generally waterproof, anti-magnetic, and high-temperature resistant, ensuring stability during application. In terms of usage, RFID has advantages in real-time data updating, information storage capacity, lifespan, work efficiency, and security. For example, RFID can conveniently update existing data while reducing manpower, material, and financial costs, making work more efficient. RFID can store information on computers, reaching up to several megabytes, ensuring smooth workflow. With careful handling, RFID can be reused multiple times, offering long service life. RFID also overcomes the previous inconvenience of information processing, allowing multiple targets to be identified simultaneously, greatly improving work efficiency. Moreover, RFID uses password protection, making it difficult to counterfeit and enhancing security.
Since establishing its RFID workshop, our company has been aiming to use RFID to enhance internal production efficiency and has developed related solutions and management procedures in the areas of warehouse material management and fixed asset inventory.
RFID Fixed Asset Management
The RFID fixed asset management system includes asset addition, modification, disposal, damage, depreciation, lending, return, allocation to departments, department usage adjustments, administrator settings, inter-department asset transfer, various report printing, and combined queries. For each fixed asset, the system can provide comprehensive information from purchase, accounting entry, usage, department assignment, depreciation status, to disposal. This dynamic query function ensures that managers can access complete information immediately; batch depreciation of assets can reduce repetitive work and ensure data accuracy; automatic report generation and printing is fast and accurate, saving considerable time compared to manual report preparation. The specific implementation plan is shown in Table 1.
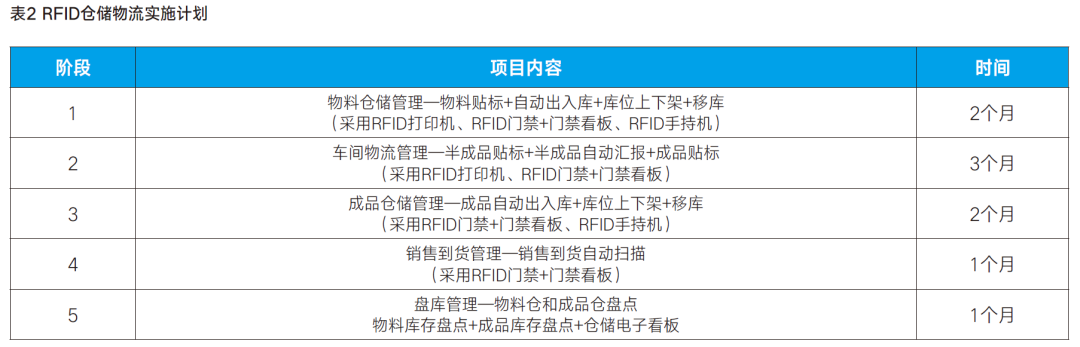
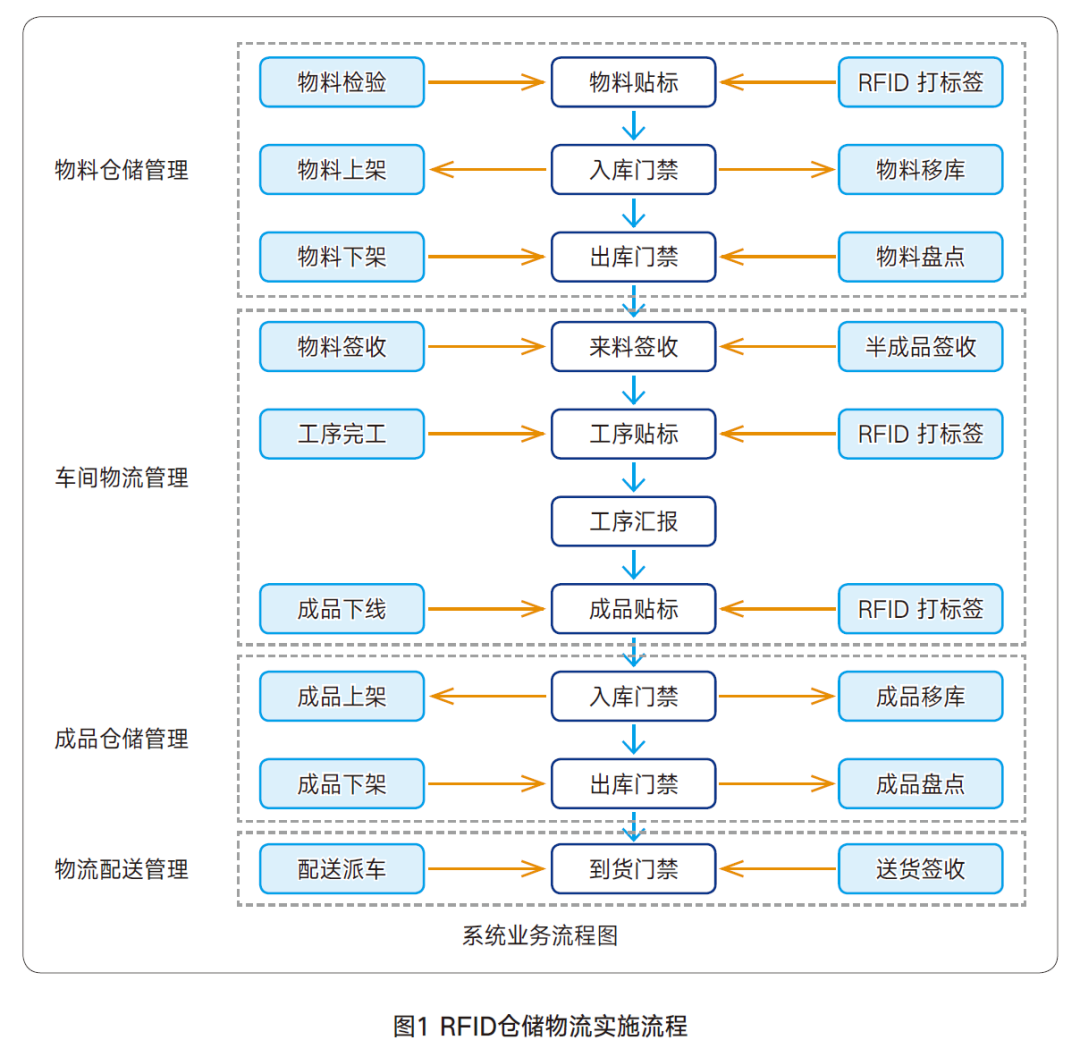
After the relevant data of each newly purchased asset is entered into the computer, the information is written into the RFID electronic tag through the corresponding software, including the name of the fixed asset, purchase date, and the department responsible for its custody (use). Then, the RFID electronic tag is attached to the physical fixed asset, which not only clearly distinguishes the department using the fixed asset but also greatly facilitates management processes such as inventory. Inventory personnel no longer need to check assets by recording asset codes and verifying ledgers; they can quickly manage inventory by simply reading the RFID tags on the fixed assets with a handheld RFID device from a distance.RFID Warehouse and Logistics ManagementRFID-based warehouse and logistics management can achieve automatic, real-time, and accurate business data collection based on RFID technology. It can enhance warehouse management levels and achieve the 'three consistencies' (consistency between accounts and inventory quantities, consistency between accounts and inventory locations, and consistency between types and quantities of goods in and out of the warehouse). It can standardize and optimize on-site operational processes, introduce error-proofing mechanisms to help managers reduce operational mistakes, and improve accuracy. It can coordinate with logistics delivery scanning systems to establish a traceability chain for goods, helping companies meet the quality traceability requirements throughout the product lifecycle. It can establish a logistics exception warning mechanism to improve the efficiency and accuracy of problem handling and reduce production costs. It can create a visualized on-site management and monitoring system to obtain real-time KPI performance indicators for logistics processes, providing senior management with comprehensive and timely firsthand data. It can also integrate with ERP systems to improve processing efficiency and accuracy.During the preparation phase, we mainly divided the work into five stages, as shown in Table 2. The implementation process is illustrated in Figure 1, with an example of finished product inbound and outbound management shown in Figure 2.
The business process for RFID material outbound is as follows: (1) Locate the finished product storage location for outbound. Retrieve the RFID tag information of the finished product storage location from the ERP system according to the delivery order number, and the system automatically queries the storage location information. (2) Remove from storage location. The forklift moves to the storage location specified by the system, verifies whether the finished product matches the delivery order, and if it does, the RFID handheld device reads the RFID tag of the finished product and retrieves the goods. (3) Outbound. The forklift moves to the warehouse gate, and the RFID access control device reads the RFID tags of the finished products in bulk. The access control display shows the outbound finished product information, and sends a command to the system indicating successful outbound, updating the finished product status.
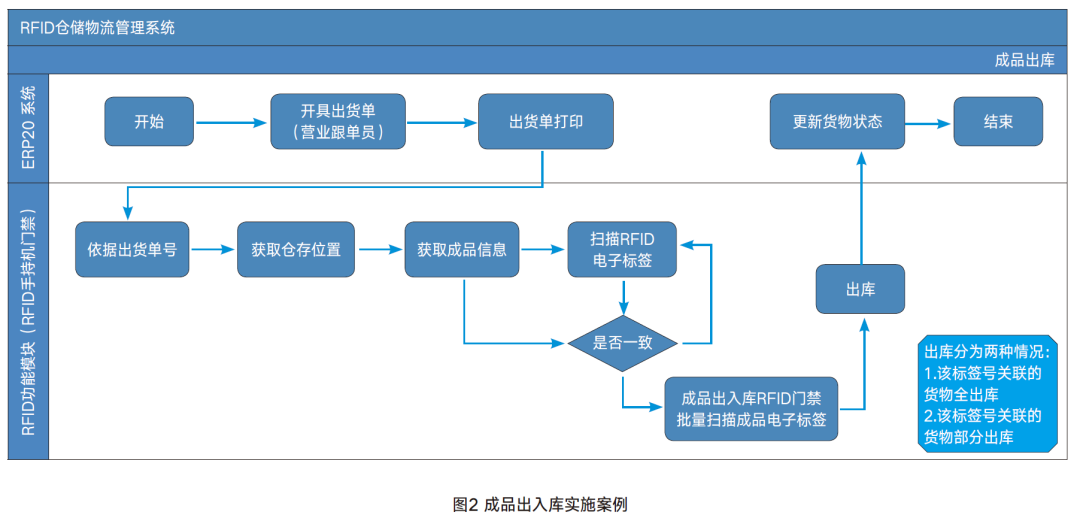
The hardware devices used in the material outbound process include RFID handheld devices, RFID access gates, storage location RFID tags, and finished product RFID tags. The above process is also applicable to semi-finished products, transfers, and other operations.
Although the implementation of RFID fixed asset inventory and warehouse material management projects has some impact on employees' original work, such as the increased workload during inbound operations, which makes it difficult for employees to accept initially, after using it for a period of time, incidents of lost or misplaced goods have significantly decreased, and inventory efficiency has greatly improved. Therefore, we firmly believe that logistics warehousing and fixed asset inventory will be the most promising areas for RFID applications. We believe that the ongoing project development will bring increasing convenience to the company and employees, and we are confident that this solution will be helpful to other enterprises with similar needs.

