Printing Technology Articles | Things About Color Management
The original intention of color management is to use color management tools to reduce prepress preparation time, minimize waste, and improve production efficiency.However, reality often falls short of expectations. Even with significant investment in manpower and resources, the results are not obvious and far from what was hoped for. Why is that?Many times, our understanding of color management is somewhat one-sided. Some think that installing prepress digital proofing is color management; some think that implementing CIP3/4 connections in prepress and printing is color management; others think that correcting printing plate curves is color management...In fact, color management is a systematic project. It requires close collaboration between prepress and printing, establishing color standards through a series of testing instruments and color management software, and performing regular maintenance to achieve the established standards.As shown in the figure above, this is a color management flowchart I summarized, which outlines the process of color management.Next, let's take a closer look:
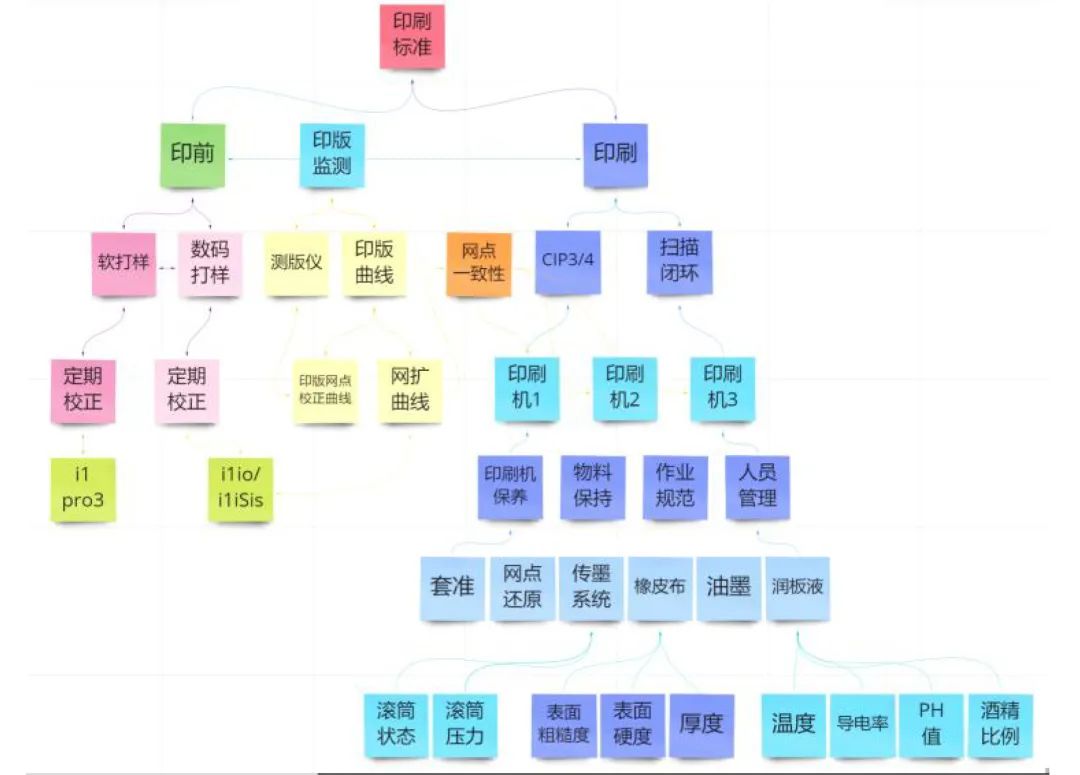
As shown in the figure above, this is a flowchart of color management that I have summarized, outlining the process of color management. Let's take a closer look:01At the top of the figure is the printing color standard. This can be a custom color standard of our factory, a target standard required by the client, or an international standard, such as ISO 12647-2. The color control workflow described below is all carried out around this target.02Once the target is determined, the process starts from prepress. First, soft proofing is used to match the printing standard. By calibrating professional monitors, loading color correction ICC profiles, and using ICC profiles for the printing standard, the colors displayed on the screen can be made consistent with the printing color standard.03The prepress digital proofing system consists of a wide-gamut printer, color management software, and color measurement instruments. The printer prints color patches, such as TC1617, and color measurement instruments like i1iO (as shown in the figure) are used to measure the colors of the patches. The results are fed back to the color management software, compared with the target printing colors, and if the color difference exceeds the tolerance range, the software adjusts the color ratios according to the color difference values. Then a second print is made... the process loops until the digital proof matches the printing standard.

04
Whether it is soft proofing or digital proofing, regular inspection and calibration must be carried out to ensure that colors are always consistent and meet printing standards. If the colors cannot meet the standards or are unstable, changes to the printing conditions should be considered to achieve compliance.05After soft proofing and digital proofing meet the standards, we need to inspect the printing plates. There are two main points to note: first, by standardizing prepress publishing operations and supporting the plate curves, the deviation of the halftone dots on the printing plate can be kept within tolerance, for example, deviations not exceeding 0.5%; second, regular inspections must be performed to ensure that every printing plate meets the standards. If problems are found, they must be addressed immediately.06Next is the standardized management of the printing press.First is the standardized management of the fountain solution: parameters such as pH value, conductivity, alcohol ratio, and water tank temperature. Second is the standardization of the ink transfer system: including whether the water and ink rollers meet standards, whether the pressure of the water-ink rollers meets standards, as well as the condition of the bearings, and ink transfer parameters. Then comes the standardization of the blanket parameters: blanket elasticity, hardness, changes in elasticity after prolonged use, including the pads (underliners) beneath the blanket, whether special or general paper. Other blanket parameters include surface roughness/surface hardness (too high may cause "blisters" or "bars" during printing, too low may cause image distortion), thickness loss rate, print durability, and so on. Other aspects, including registration accuracy, ink fountain and key functions, water tank cooling and fountain solution circulation and replenishment functions, must all be standardized and qualified.Only after standardized management of the printing press internal parameters has been carried out and quantitative metrics meet the standards can the next step of printing standard matching be performed, which will then be meaningful.07Next, we perform printing standard matching for the press.Using printing test sheets or other methods, we first test whether the color differences for solid colors such as CMYK and RGB meet standards. If not, consider changing the ink or paper. Next, by obtaining the correct dot gain and gray balance plate curve, we reprint the plates to achieve the correct dot gain and gray balance. Finally, using the printing press along with color management software and color measuring instruments, the printed colors of the press are matched to the printing target. Record the standard density and obtain the ICC profile of the press.08After the printing standard matching is completed on the first press, we proceed with horizontal operations on the second, third press, and so on. The method is the same as the first press, but attention must be paid to the following:1. Ensure that each press's dot gain and gray balance plate curve correspond correctly; do not mix them up.2. Clearly and correctly manage the prepress machine's dot correction curve and the press's dot gain and gray balance plate curve, understand their functions, and do not use them incorrectly.09Maintain consistency in printing conditions: such as printing materials like ink and fountain solution, prepress plates, development, ink, digital proofing paper; operational methods, such as printing color sequence; and paper brands, etc. Changes in printing conditions during the printing process (including prepress) will affect the success of color management.10As with prepress, after completing printing standard matching on the press, regular maintenance of the machines should be carried out according to the standardized management of the press, ensuring parameters meet standards and conducting quantitative monitoring. Printing standard matching should be carried out regularly to correct deviations, verify alignment with printing standards, and maintain consistency with printing standards.
11
On this basis, in order to improve production efficiency, we connect CIP3/4 and generate pre-inking curves according to printing standards. Such pre-inking is efficient. Additionally, a scanning and closed-loop system can be installed (as shown below): the scanning system detects the difference between the current color and the target parameters, and the closed-loop system is a computer that intelligently adjusts the ink keys of the printing press to quickly achieve the target color. This reduces paper waste, improves production efficiency, and enhances color quality.

SummaryIn conclusion, regarding the matters of printing color management, I hope everyone can effectively manage this comprehensive color management system, with each link closely connected, forming an efficient and accurate color closed loop. The goal is to improve color quality, reduce waste of paper, ink, and labor, and enhance work efficiency.

