Application of Algal Polysaccharides in Food Packaging
Currently, plastic pollution is gradually becoming the world's second most pressing environmental issue after climate change, posing great challenges to global sustainable development. China is the largest producer and consumer of plastics in the world. Synthetic plastics made from petroleum products are widely used in the food packaging industry. Traditional plastic packaging is often non-recyclable, non-biodegradable, and has poor reusability, leading to the rapid accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans, causing serious environmental and health problems. In addition, microplastics and toxic additives in plastics can also accumulate through the food chain.
Biodegradable packaging materials made from biopolymers can replace non-biodegradable petroleum-based packaging materials, reducing environmental pollution. Among biopolymers, polysaccharides are abundant, low-cost, non-toxic, renewable, and environmentally friendly. Algal polysaccharides such as carrageenan, alginate, agar, and ulvan have biological activities such as antiviral, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor, and immune-regulating properties, and are widely used in medicine, food, cosmetics, and other fields. At the same time, algal polysaccharides have good film-forming properties, certain mechanical strength, and good gas barrier performance, making them suitable for developing eco-friendly plastic packaging that ensures food quality and microbial safety.
Generally, algal polysaccharides are often applied in food packaging materials in the form of polysaccharide composites. Methods to modify polysaccharide-based polymers include chemical modification of polysaccharides, adding natural or chemical additives (such as plasticizers, surfactants, anti-browning agents, etc.), blending with different types of polymers, designing multilayer films, and adding nanoparticles. These methods can produce polysaccharide composite materials used to develop new types of food packaging.
01
Edible Films and Coatings
Thakur et al. [2] used rice starch/ι-carrageenan/stearic acid/glycerol/Tween 20 to create an edible coating with high tensile strength (116.5 N/m²), moderate solubility (63.22%), and low water vapor permeability (3.55×10⁻¹¹ g·Pa⁻¹·s⁻¹·m⁻¹), forming an edible, preservative coating on the surface of fruits.
Peretto et al. [3] prepared an edible coating using sodium alginate/parsley phenol/methyl cinnamate, which can be applied to fresh strawberries using electrostatic spraying or brushing methods. Compared with conventional non-electrostatic spraying methods, this approach improves fruit firmness and other mechanical properties, while providing higher natural antimicrobial activity, better preserving the freshness of strawberries.
02
Active Packaging
Active packaging not only provides an inert barrier against external conditions but also plays an important role in food preservation and quality monitoring. Active compounds in active packaging can remove moisture, carbon dioxide, oxygen, or ethylene from food or the environment, or provide antibacterial, antioxidant, and flavor-enhancing effects.
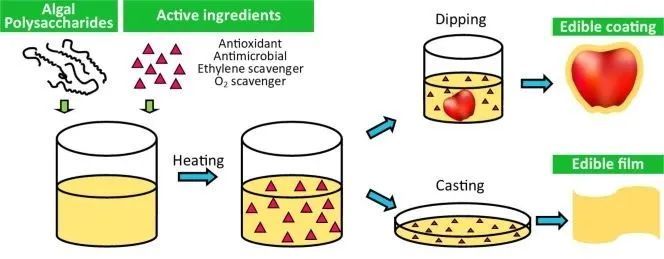
Figure 1 Edible Films and Coatings for Active Packaging Based on Algal Polysaccharides [1]
Edible films prepared from κ- and ι-carrageenan, glycerol, and Lapacho extract have good antioxidant activity, which helps extend the shelf life of fruits and vegetables [4]. Antimicrobial films made from agar and nisin from Lactobacillus in sake can replace traditional aluminum foil used in cheese packaging [5]. Adding antibacterial metal nanoparticles to polysaccharide composite films can significantly enhance antimicrobial effects. Active food packaging films developed from pullulan/carrageenan CuS nanoparticles/D-limonene exhibit good antibacterial activity against foodborne pathogens [6]. Ultraviolet light is a major factor promoting food aging and spoilage. Yang et al. [7] developed active films with UV-blocking and thermal insulation properties by integrating bio-inspired dopamine-melanin solid nanoparticles into sodium alginate/polyvinyl alcohol films.
03
Intelligent Packaging
Intelligent packaging can provide consumers with quick, non-destructive, real-time information on the quality and safety of packaged foods.
Among these, colorimetric pH sensor films offer a safe, non-destructive method to visually assess food freshness during storage. Colorimetric pH sensor films developed from ι-carrageenan and natural mixed dyes exhibit clear color changes (red-purple-blue-green-yellow) across a pH range of 1.0-12.0, and can be used to detect food spoilage [8]. Colorimetric films prepared by incorporating raspberry pomace extract into pectin/sodium alginate/xanthan gum composite films show noticeable color changes from pink-red-brown-blue-dark green in the pH range of 5-10, making them useful for detecting the freshness of protein-rich foods [9].
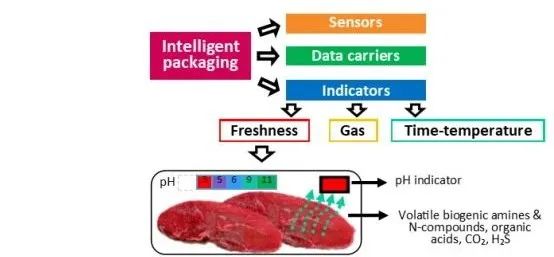
Figure 2 Schematic of Smart Packaging and Freshness Indicators

